On Linux/Unix platforms, the 'ls' command is one of the most frequently used commands. This should be one of the first commands you train when you enter the shell/command prompt.
This guide will teach you how to use the various options of 'ls' command. All the below examples of the 'ls' command are tested on RHEL/CENTOS 7.6.
Global Syntax ls command with options:
ls [OPTION] [File]
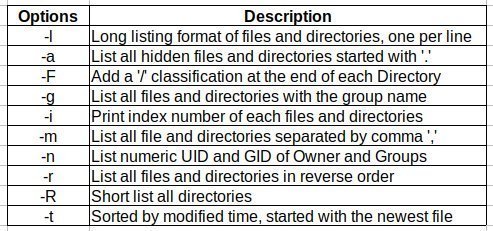
There are a lot of options available using the 'ls' command, but we will be looking at the most used and combined possible options only. The following tabular gives you the possible options and functions in the 'ls' command:
1. How to list files using 'ls' with no option?
# ls
Output:
anaconda cron-20190721 glusterfs maillog-20190804 pluto secure-20190730
sssd Xorg.9.log audit cron-20190730 httpd mariadb ppp
Note: Using the 'ls' command with no option will simply list all files and directories. You cannot see any other information.
2. How to long list one per line for all files and directories?
# ls -l
output:

# ls -a
output:

4. How to list Directories with '/' classification at the end?
# ls -F
output:

5. How to list all the files and directories without the owner details?
# ls -g
output:

6. How to list the index (inode) number of each File and Directory?
# ls -i
output:

7. How to list the files and directories separated by a comma?
#ls -m
output:

8. How to list UID and GID of files and directories?
# ls -n
output:
9. How to list all the files and directories in reverse order?
# ls -r
output:
Note: The 'ls -r' option will list all files and directories in reverse order. In the above example you can see, all the files and directories are sorted in reverse alphabetical order.
10. How to get a recursive listing of all sub-directories?
# ls -lR
output:

11. How to list the most recently modified files and folders?
# ls -t
output:
Note: Option 'ls -t' will list out all the recently modified files and folders first. In the above example you can see a folder named 'linuxteck' and a file named 'test' are listed in the first place. These two files are the newly created ones.
12. How to list the size of the files in a human-readable format?
# ls -lh
output:

In addition, the ls command won't display the total amount of space taken up by the contents of the directory. In order to determine the size of any directory, you can use the du command
13. How to list a particular file details?
# ls -l cron.txt
output:

14. How to list a particular directory details?
# ls -ld testing/
output:

15. How to list the files under a directory?
# ls -l Desktop/
output:

16. How to list files and directories sorted by file-size?
# ls -lS
output:

17. How to list the version of the ls command?
# ls --v OR # ls --version
output:
Please refer to the manual page using the below commands to explore in-depth
# man ls
# info ls
I hope this article will help you to learn a few options of 'ls' commands in Linux! Drop me your feedback/comments and please share if you like 🙂
A few ls references are collected from this site
Thank you!






